Joseph Louis Lagrange
| Joseph-Louis Lagrange | |
|---|---|
 Joseph-Louis (Giuseppe Lodovico),
comte de Lagrange |
|
| Born | 25 January 1736 Turin, Piedmont |
| Died | 10 April 1813 (aged 77) Paris, France |
| Residence | Piedmont France Prussia |
| Nationality | Italian French |
| Fields | Mathematics Mathematical physics |
| Institutions | École Polytechnique |
| Doctoral advisor | Leonhard Euler |
| Doctoral students | Joseph Fourier Giovanni Plana Siméon Poisson |
| Known for | Analytical mechanics Celestial mechanics Mathematical analysis Number theory |
|
Notes
Note he did not have a doctoral advisor but academic genealogy authorities link his intellectual heritage to Leonhard Euler, who played the equivalent role. |
|
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (25 January 1736, Turin, Piedmont – 10 April 1813, Paris), born Giuseppe Lodovico (Luigi) Lagrangia, was an Italian-born mathematician and astronomer, who lived part of his life in Prussia and part in France, making significant contributions to all fields of analysis, to number theory, and to classical and celestial mechanics. On the recommendation of Euler and D'Alembert, in 1766 Lagrange succeeded Euler as the director of mathematics at the Prussian Academy of Sciences in Berlin, where he stayed for over twenty years, producing a large body of work and winning several prizes of the French Academy of Sciences. Lagrange's treatise on analytical mechanics (Mécanique Analytique, 4. ed., 2 vols. Paris: Gauthier-Villars et fils, 1888-89), written in Berlin and first published in 1788, offered the most comprehensive treatment of classical mechanics since Newton and formed a basis for the development of mathematical physics in the nineteenth century.
Born Giuseppe Lodovico Lagrangia in Turin of Italian parents, Lagrange had French ancestors on his father's side. In 1787, at age 51, he moved from Berlin to France and became a member of the French Academy, and he remained in France until the end of his life. Therefore, Lagrange is alternatively considered a French and an Italian scientist. Lagrange survived the French Revolution and became the first professor of analysis at the École Polytechnique upon its opening in 1794. Napoleon named Lagrange to the Legion of Honour and made him a Count of the Empire in 1808. He is buried in the Panthéon.
Contents |
Scientific contribution
Lagrange was one of the creators of the calculus of variations, deriving the Euler–Lagrange equations for extrema of functionals. He also extended the method to take into account possible constraints, arriving at the method of Lagrange multipliers. Lagrange invented the method of solving differential equations known as variation of parameters, applied differential calculus to the theory of probabilities and attained notable work on the solution of equations. He proved that every natural number is a sum of four squares. His treatise Theorie des fonctions analytiques laid some of the foundations of group theory, anticipating Galois. In calculus, Lagrange developed a novel approach to interpolation and Taylor series. He studied the three-body problem for the Earth, Sun, and Moon (1764) and the movement of Jupiter’s satellites (1766), and in 1772 found the special-case solutions to this problem that are now known as Lagrangian points. But above all he impressed on mechanics, having transformed Newtonian mechanics into a branch of analysis, Lagrangian mechanics as it is now called, and exhibited the so-called mechanical "principles" as simple results of the variational calculus.
Biography
Early years
Lagrange was born, of French and Italian descent (a paternal great grandfather was a French army officer who then moved to Turin)[1], as Giuseppe Lodovico Lagrangia in Turin. His father, who had charge of the Kingdom of Sardinia's military chest, was of good social position and wealthy, but before his son grew up he had lost most of his property in speculations, and young Lagrange had to rely on his own abilities for his position. He was educated at the college of Turin, but it was not until he was seventeen that he showed any taste for mathematics – his interest in the subject being first excited by a paper by Edmund Halley which he came across by accident. Alone and unaided he threw himself into mathematical studies; at the end of a year's incessant toil he was already an accomplished mathematician, and was made a lecturer in the artillery school.
Variational calculus
Lagrange is one of the founders of the calculus of variations. Starting in 1754, he worked on the problem of tautochrone, discovering a method of maximizing and minimizing functionals in a way similar to finding extrema of functions. Lagrange wrote several letters to Leonhard Euler between 1754 and 1756 describing his results. He outlined his "δ-algorithm", leading to the Euler–Lagrange equations of variational calculus and considerably simplifying Euler's earlier analysis.[2] Lagrange also applied his ideas to problems of classical mechanics, generalizing the results of Euler and Maupertuis.
Euler was very impressed with Lagrange's results. It has been stated that "with characteristic courtesy he withheld a paper he had previously written, which covered some of the same ground, in order that the young Italian might have time to complete his work, and claim the undisputed invention of the new calculus"; however, this chivalric view has been disputed.[3] Lagrange published his method in two memoirs of the Turin Society in 1762 and 1773.
Miscellanea Taurinensia
In 1758, with the aid of his pupils, Lagrange established a society, which was subsequently incorporated as the Turin Academy of Sciences, and most of his early writings are to be found in the five volumes of its transactions, usually known as the Miscellanea Taurinensia. Many of these are elaborate papers. The first volume contains a paper on the theory of the propagation of sound; in this he indicates a mistake made by Newton, obtains the general differential equation for the motion, and integrates it for motion in a straight line. This volume also contains the complete solution of the problem of a string vibrating transversely; in this paper he points out a lack of generality in the solutions previously given by Brook Taylor, D'Alembert, and Euler, and arrives at the conclusion that the form of the curve at any time t is given by the equation 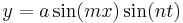 . The article concludes with a masterly discussion of echoes, beats, and compound sounds. Other articles in this volume are on recurring series, probabilities, and the calculus of variations.
. The article concludes with a masterly discussion of echoes, beats, and compound sounds. Other articles in this volume are on recurring series, probabilities, and the calculus of variations.
The second volume contains a long paper embodying the results of several papers in the first volume on the theory and notation of the calculus of variations; and he illustrates its use by deducing the principle of least action, and by solutions of various problems in dynamics.
The third volume includes the solution of several dynamical problems by means of the calculus of variations; some papers on the integral calculus; a solution of Fermat's problem mentioned above: given an integer n which is not a perfect square, to find a number x such that x2n + 1 is a perfect square; and the general differential equations of motion for three bodies moving under their mutual attractions.
The next work he produced was in 1764 on the libration of the Moon, and an explanation as to why the same face was always turned to the earth, a problem which he treated by the aid of virtual work. His solution is especially interesting as containing the germ of the idea of generalized equations of motion, equations which he first formally proved in 1780.
Berlin Academy
Already in 1756 Euler, with support from Maupertuis, made an attempt to bring Lagrange to the Berlin Academy. Later, D'Alambert interceded on Lagrange's behalf with Frederick of Prussia and wrote to Lagrange asking him to leave Turin for a considerably more prestigious position in Berlin. Lagrange turned down both offers, responding in 1765 that
- It seems to me that Berlin would not be at all suitable for me while M.Euler is there.
In 1766 Euler left Berlin for Saint Petersburg, and Frederick wrote to Lagrange expressing the wish of "the greatest king in Europe" to have "the greatest mathematician in Europe" resident at his court. Lagrange was finally persuaded and he spent the next twenty years in Prussia, where he produced not only the long series of papers published in the Berlin and Turin transactions, but his monumental work, the Mécanique analytique. His residence at Berlin commenced with an unfortunate mistake. Finding most of his colleagues married, and assured by their wives that it was the only way to be happy, he married; his wife soon died, but the union was not a happy one.
Lagrange was a favourite of the king, who used frequently to discourse to him on the advantages of perfect regularity of life. The lesson went home, and thenceforth Lagrange studied his mind and body as though they were machines, and found by experiment the exact amount of work which he was able to do without breaking down. Every night he set himself a definite task for the next day, and on completing any branch of a subject he wrote a short analysis to see what points in the demonstrations or in the subject-matter were capable of improvement. He always thought out the subject of his papers before he began to compose them, and usually wrote them straight off without a single erasure or correction.
France
In 1786, Frederick died, and Lagrange, who had found the climate of Berlin trying, gladly accepted the offer of Louis XVI to move to Paris. He received similar invitations from Spain and Naples. In France he was received with every mark of distinction and special apartments in the Louvre were prepared for his reception, and he became a member of the French Academy of Sciences, which later became part of the National Institute. At the beginning of his residence in Paris he was seized with an attack of melancholy, and even the printed copy of his Mécanique on which he had worked for a quarter of a century lay for more than two years unopened on his desk. Curiosity as to the results of the French revolution first stirred him out of his lethargy, a curiosity which soon turned to alarm as the revolution developed.
It was about the same time, 1792, that the unaccountable sadness of his life and his timidity moved the compassion of a young girl who insisted on marrying him, and proved a devoted wife to whom he became warmly attached. Although the decree of October 1793 that ordered all foreigners to leave France specifically exempted him by name, he was preparing to escape when he was offered the presidency of the commission for the reform of weights and measures. The choice of the units finally selected was largely due to him, and it was mainly owing to his influence that the decimal subdivision was accepted by the commission of 1799. In 1795, Lagrange was one of the founding members of the Bureau des Longitudes.
Though Lagrange had determined to escape from France while there was yet time, he was never in any danger; and the different revolutionary governments (and at a later time, Napoleon) loaded him with honours and distinctions. A striking testimony to the respect in which he was held was shown in 1796 when the French commissary in Italy was ordered to attend in full state on Lagrange's father, and tender the congratulations of the republic on the achievements of his son, who "had done honour to all mankind by his genius, and whom it was the special glory of Piedmont to have produced." It may be added that Napoleon, when he attained power, warmly encouraged scientific studies in France, and was a liberal benefactor of them.
École normale
In 1795, Lagrange was appointed to a mathematical chair at the newly established École normale, which enjoyed only a brief existence of four months. His lectures here were quite elementary, and contain nothing of any special importance, but they were published because the professors had to "pledge themselves to the representatives of the people and to each other neither to read nor to repeat from memory," and the discourses were ordered to be taken down in shorthand in order to enable the deputies to see how the professors acquitted themselves.
École Polytechnique
Lagrange was appointed professor of the École Polytechnique in 1794; and his lectures there are described by mathematicians who had the good fortune to be able to attend them, as almost perfect both in form and matter. Beginning with the merest elements, he led his hearers on until, almost unknown to themselves, they were themselves extending the bounds of the subject: above all he impressed on his pupils the advantage of always using general methods expressed in a symmetrical notation.
On the other hand, Fourier, who attended his lectures in 1795, wrote:
- His voice is very feeble, at least in that he does not become heated; he has a very pronounced Italian accent and pronounces the s like z … The students, of whom the majority are incapable of appreciating him, give him little welcome, but the professors make amends for it.
Late years

In 1810, Lagrange commenced a thorough revision of the Mécanique analytique, but he was able to complete only about two-thirds of it before his death in 1813. He was buried that same year in the Panthéon in Paris. The French inscription on his tomb there reads:
JOSEPH LOUIS LAGRANGE. Senator. Count of the Empire. Grand Officer of the Legion of Honour. Grand Cross of the Imperial Order of Réunion. Member of the Institute and the Bureau of Longitude. Born in Turin on 25 January 1736. Died in Paris on 10 April 1813.
Work in Berlin
Lagrange was extremely active scientifically during twenty years he spent in Berlin. Not only did he produce his splendid Mécanique analytique, but he contributed between one and two hundred papers to the Academy of Turin, the Berlin Academy, and the French Academy. Some of these are really treatises, and all without exception are of a high order of excellence. Except for a short time when he was ill he produced on average about one paper a month. Of these, note the following as amongst the most important.
First, his contributions to the fourth and fifth volumes, 1766–1773, of the Miscellanea Taurinensia; of which the most important was the one in 1771, in which he discussed how numerous astronomical observations should be combined so as to give the most probable result. And later, his contributions to the first two volumes, 1784–1785, of the transactions of the Turin Academy; to the first of which he contributed a paper on the pressure exerted by fluids in motion, and to the second an article on integration by infinite series, and the kind of problems for which it is suitable.
Most of the papers sent to Paris were on astronomical questions, and among these one ought to particularly mention his paper on the Jovian system in 1766, his essay on the problem of three bodies in 1772, his work on the secular equation of the Moon in 1773, and his treatise on cometary perturbations in 1778. These were all written on subjects proposed by the Académie française, and in each case the prize was awarded to him.
Lagrangian mechanics
| Classical mechanics | ||||||||||
History of classical mechanics · Timeline of classical mechanics
|
||||||||||
Between 1772 and 1788, Lagrange re-formulated Classical/Newtonian mechanics to simplify formulas and ease calculations. These mechanics are called Lagrangian mechanics.
Algebra
The greater number of his papers during this time were, however, contributed to the Prussian Academy of Sciences. Several of them deal with questions in algebra.
- His discussion of representations of integers by quadratic forms (1769) and by more general algebraic forms (1770).
- His tract on the Theory of Elimination, 1770.
- Lagrange's theorem that the order of a subgroup H of a group G must divide the order of G.
- His papers of 1770 and 1771 on the general process for solving an algebraic equation of any degree via the Lagrange resolvents. This method fails to give a general formula for solutions of an equation of degree five and higher, because the auxiliary equation involved has higher degree than the original one. The significance of this method is that it exhibits the already known formulas for solving equations of second, third, and fourth degrees as manifestations of a single principle, and was foundational in Galois theory. The complete solution of a binomial equation of any degree is also treated in these papers.
- In 1773, Lagrange considered a functional determinant of order 3, a special case of a Jacobian. He also proved the expression for the volume of a tetrahedron with one of the vertices at the origin as the one sixth of the absolute value of the determinant formed by the coordinates of the other three vertices.
Number Theory
Several of his early papers also deal with questions of number theory.
- Lagrange (1766–1769) was the first to prove that Pell's equation
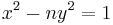 has a nontrivial solution in the integers for any non-square natural number n.[4]
has a nontrivial solution in the integers for any non-square natural number n.[4] - He proved the theorem, stated by Bachet without justification, that every positive integer is the sum of four squares, 1770.
- He proved Wilson's theorem that if n is a prime, then (n − 1)! + 1 is always a multiple of n, 1771.
- His papers of 1773, 1775, and 1777 gave demonstrations of several results enunciated by Fermat, and not previously proved.
- His Recherches d'Arithmétique of 1775 developed a general theory of binary quadratic forms to handle the general problem of when an integer is representable by the form
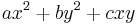 .
.
Other mathematical work
There are also numerous articles on various points of analytical geometry. In two of them, written rather later, in 1792 and 1793, he reduced the equations of the quadrics (or conicoids) to their canonical forms.
During the years from 1772 to 1785, he contributed a long series of papers which created the science of partial differential equations. A large part of these results were collected in the second edition of Euler's integral calculus which was published in 1794.
He made contributions to the theory of continued fractions.
Astronomy
Lastly, there are numerous papers on problems in astronomy. Of these the most important are the following:
- Attempting to solve the three-body problem resulting in the discovery of Lagrangian points, 1772
- On the attraction of ellipsoids, 1773: this is founded on Maclaurin's work.
- On the secular equation of the Moon, 1773; also noticeable for the earliest introduction of the idea of the potential. The potential of a body at any point is the sum of the mass of every element of the body when divided by its distance from the point. Lagrange showed that if the potential of a body at an external point were known, the attraction in any direction could be at once found. The theory of the potential was elaborated in a paper sent to Berlin in 1777.
- On the motion of the nodes of a planet's orbit, 1774.
- On the stability of the planetary orbits, 1776.
- Two papers in which the method of determining the orbit of a comet from three observations is completely worked out, 1778 and 1783: this has not indeed proved practically available, but his system of calculating the perturbations by means of mechanical quadratures has formed the basis of most subsequent researches on the subject.
- His determination of the secular and periodic variations of the elements of the planets, 1781-1784: the upper limits assigned for these agree closely with those obtained later by Le Verrier, and Lagrange proceeded as far as the knowledge then possessed of the masses of the planets permitted.
- Three papers on the method of interpolation, 1783, 1792 and 1793: the part of finite differences dealing therewith is now in the same stage as that in which Lagrange left it.
Mécanique analytique
Over and above these various papers he composed his great treatise, the Mécanique analytique. In this he lays down the law of virtual work, and from that one fundamental principle, by the aid of the calculus of variations, deduces the whole of mechanics, both of solids and fluids.
The object of the book is to show that the subject is implicitly included in a single principle, and to give general formulae from which any particular result can be obtained. The method of generalized co-ordinates by which he obtained this result is perhaps the most brilliant result of his analysis. Instead of following the motion of each individual part of a material system, as D'Alembert and Euler had done, he showed that, if we determine its configuration by a sufficient number of variables whose number is the same as that of the degrees of freedom possessed by the system, then the kinetic and potential energies of the system can be expressed in terms of those variables, and the differential equations of motion thence deduced by simple differentiation. For example, in dynamics of a rigid system he replaces the consideration of the particular problem by the general equation, which is now usually written in the form
where  represents the kinetic energy and
represents the kinetic energy and 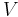 represents the potential energy of the system. He then presented what we now know as the method of Lagrange multipliers—though this is not the first time that method was published—as a means to solve this equation.[5] Amongst other minor theorems here given it may mention the proposition that the kinetic energy imparted by the given impulses to a material system under given constraints is a maximum, and the principle of least action. All the analysis is so elegant that Sir William Rowan Hamilton said the work could only be described as a scientific poem. It may be interesting to note that Lagrange remarked that mechanics was really a branch of pure mathematics analogous to a geometry of four dimensions, namely, the time and the three coordinates of the point in space; and it is said that he prided himself that from the beginning to the end of the work there was not a single diagram. At first no printer could be found who would publish the book; but Legendre at last persuaded a Paris firm to undertake it, and it was issued under his supervision in 1788.
represents the potential energy of the system. He then presented what we now know as the method of Lagrange multipliers—though this is not the first time that method was published—as a means to solve this equation.[5] Amongst other minor theorems here given it may mention the proposition that the kinetic energy imparted by the given impulses to a material system under given constraints is a maximum, and the principle of least action. All the analysis is so elegant that Sir William Rowan Hamilton said the work could only be described as a scientific poem. It may be interesting to note that Lagrange remarked that mechanics was really a branch of pure mathematics analogous to a geometry of four dimensions, namely, the time and the three coordinates of the point in space; and it is said that he prided himself that from the beginning to the end of the work there was not a single diagram. At first no printer could be found who would publish the book; but Legendre at last persuaded a Paris firm to undertake it, and it was issued under his supervision in 1788.
Work in France
Differential calculus and calculus of variations
Lagrange's lectures on the differential calculus at École Polytechnique form the basis of his treatise Théorie des fonctions analytiques, which was published in 1797. This work is the extension of an idea contained in a paper he had sent to the Berlin papers in 1772, and its object is to substitute for the differential calculus a group of theorems based on the development of algebraic functions in series. A somewhat similar method had been previously used by John Landen in the Residual Analysis, published in London in 1758. Lagrange believed that he could thus get rid of those difficulties, connected with the use of infinitely large and infinitely small quantities, to which philosophers objected in the usual treatment of the differential calculus. The book is divided into three parts: of these, the first treats of the general theory of functions, and gives an algebraic proof of Taylor's theorem, the validity of which is, however, open to question; the second deals with applications to geometry; and the third with applications to mechanics. Another treatise on the same lines was his Leçons sur le calcul des fonctions, issued in 1804, with the second edition in 1806. It is in this book that Lagrange formulated his celebrated method of Lagrange multipliers, in the context of problems of variational calculus with integral constraints. These works devoted to differential calculus and calculus of variations may be considered as the starting point for the researches of Cauchy, Jacobi, and Weierstrass.
Infinitesimals
At a later period Lagrange reverted to the use of infinitesimals in preference to founding the differential calculus on the study of algebraic forms; and in the preface to the second edition of the Mécanique, which was issued in 1811, he justifies the employment of infinitesimals, and concludes by saying that:
- When we have grasped the spirit of the infinitesimal method, and have verified the exactness of its results either by the geometrical method of prime and ultimate ratios, or by the analytical method of derived functions, we may employ infinitely small quantities as a sure and valuable means of shortening and simplifying our proofs.
Continued fractions
His Résolution des équations numériques, published in 1798, was also the fruit of his lectures at École Polytechnique. There he gives the method of approximating to the real roots of an equation by means of continued fractions, and enunciates several other theorems. In a note at the end he shows how Fermat's little theorem that
- ap−1 − 1 ≡ 0 (mod p)
where p is a prime and a is prime to p, may be applied to give the complete algebraic solution of any binomial equation. He also here explains how the equation whose roots are the squares of the differences of the roots of the original equation may be used so as to give considerable information as to the position and nature of those roots.
The theory of the planetary motions had formed the subject of some of the most remarkable of Lagrange's Berlin papers. In 1806 the subject was reopened by Poisson, who, in a paper read before the French Academy, showed that Lagrange's formulae led to certain limits for the stability of the orbits. Lagrange, who was present, now discussed the whole subject afresh, and in a letter communicated to the Academy in 1808 explained how, by the variation of arbitrary constants, the periodical and secular inequalities of any system of mutually interacting bodies could be determined.
Prizes and distinctions
Euler proposed Lagrange for election to the Berlin Academy and he was elected on 2 September 1756. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1790, a Fellow of the Royal Society and a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1806. In 1808, Napoleon made Lagrange a Grand Officer of the Legion of Honour and a Comte of the Empire. He was awarded the Grand Croix of the Ordre Impérial de la Réunion in 1813, a week before his death in Paris.
Lagrange was awarded the 1764 prize of the French Academy of Sciences for his memoir on the libration of the Moon. In 1766 the Academy proposed a problem of the motion of the satellites of Jupiter, and the prize again was awarded to Lagrange. He also won the prizes of 1772, 1774, and 1778.
Lagrange is one of the 72 prominent French scientists who were commemorated on plaques at the first stage of the Eiffel Tower when it first opened. Rue Lagrange in the 5th Arrondissement in Paris is named after him. In Turin, the street where the house of his birth still stands is named via Lagrange. The lunar crater Lagrange also bears his name.
Apocrypha
- He was of medium height and slightly formed, with pale blue eyes and a colorless complexion. He was nervous and timid, he detested controversy, and, to avoid it, willingly allowed others to take credit for what he had done himself.[6]
- Due to thorough preparation, he was usually able to write out his papers complete without a single crossing-out or correction.[6]
See also
- List of topics named after Joseph Louis Lagrange
Notes
The initial version of this article was taken from the public domain resource A Short Account of the History of Mathematics (4th edition, 1908) by W. W. Rouse Ball.
- ↑ Lagrange biography
- ↑ Although some authors speak of general method of solving "isoperimetric problems", the eighteenth century meaning of this expression amounts to "problems in variational calculus", reserving the adjective "relative" for problems with isoperimetric-type constraints. The celebrated method of Lagrange multipliers, which applies to optimization of functions of several variables subject to constraints, did not appear until much later, see Craig Fraser, Isoperimetric Problems in the Variational Calculus of Euler and Lagrange, Historia Mathematica, 19(1992), pp.4–23.
- ↑ Galletto, D., The genesis of Mècanique analytique, La Mècanique analytique de Lagrange et son héritage, II (Turin, 1989). Atti Accad. Sci. Torino Cl. Sci. Fis. Mat. Natur. 126 (1992), suppl. 2, 277--370, MR1264671.
- ↑ Oeveres, t.1, 671–732
- ↑ Marco Panza, "The Origins of Analytic Mechanics in the 18th Century", in Hans Niels Jahnke (editor), A History of Analysis, 2003, p. 149
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 W. W. Rouse Ball, 1908, "Joseph Louis Lagrange (1736 - 1813)," A Short Account of the History of Mathematics, 4th ed. pp. 401 - 412
References
- Columbia Encyclopedia, 6th ed., 2005, "Lagrange, Joseph Louis."
- W. W. Rouse Ball, 1908, "Joseph Louis Lagrange (1736 - 1813)," A Short Account of the History of Mathematics, 4th ed.
- Chanson, Hubert, 2007, "Velocity Potential in Real Fluid Flows: Joseph-Louis Lagrange's Contribution," La Houille Blanche 5: 127-31.
- Fraser, Craig G., 2005, "Théorie des fonctions analytiques" in Grattan-Guinness, I., ed., Landmark Writings in Western Mathematics. Elsevier: 258-76.
- Lagrange, Joseph-Louis. (1811). Mecanique Analytique. Courcier (reissued by Cambridge University Press, 2009; ISBN 9781108001748)
- Lagrange, J.L. (1781) "Mémoire sur la Théorie du Mouvement des Fluides"(Memoir on the Theory of Fluid Motion) in Serret, J.A., ed., 1867. Oeuvres de Lagrange, Vol. 4. Paris" Gauthier-Villars: 695-748.
- Pulte, Helmut, 2005, "Méchanique Analytique" in Grattan-Guinness, I., ed., Landmark Writings in Western Mathematics. Elsevier: 208-24.
External links
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Joseph Louis Lagrange", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Lagrange.html.
- Weisstein, Eric W., Lagrange, Joseph (1736-1813) from ScienceWorld.
- Lagrange, Joseph Louis de: The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy and Space Flight
- Joseph Louis Lagrange at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- The Founders of Classical Mechanics: Joseph Louis Lagrange
- The Lagrange Points
- Lagrange's works (in French) Oeuvres de Lagrange, edited by Joseph Alfred Serret, Paris 1867, digitized by Göttinger Digitalisierungszentrum (Mécanique analytique is in volumes 11 and 12.)
- Rue Lagrange, Paris